RBI MPC Meeting 2024: Key Decisions and Initiatives Unveiled
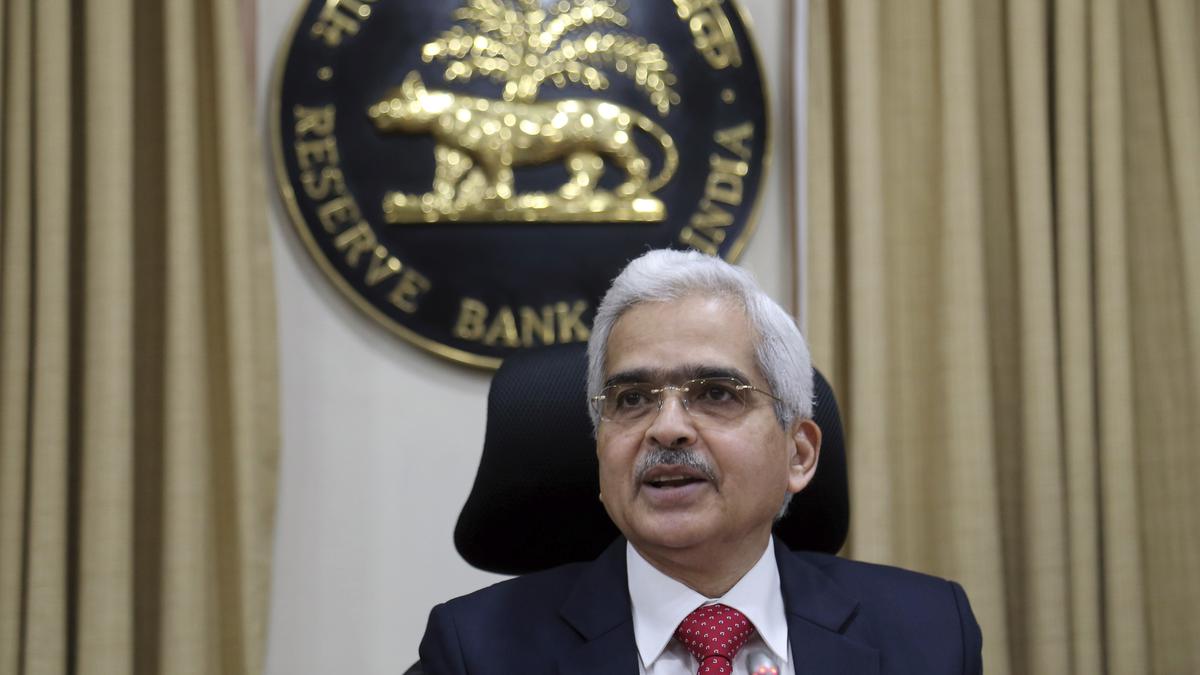
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) Governor, Shaktikanta Das, recently announced the outcomes of the first monetary policy meeting for the financial year 2024-25. The two-day review conducted by the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), the rate-setting panel, culminated in several significant decisions aimed at steering the nation’s economy amidst evolving global and domestic dynamics.
Policy Measures:
Repo Rate Unchanged: The RBI has opted to maintain the key policy repo rate at 6.5%, marking the seventh consecutive instance of status quo in this regard.
Policy Stance: The MPC has decided to sustain the policy stance at ‘withdrawal of accommodation,’ signaling a cautious approach towards monetary policy adjustments amidst prevailing economic conditions.
GDP Growth Projection: India’s real GDP growth rate for the fiscal year 2024-25 is forecasted at 7%. The quarterly projections indicate a consistent growth trajectory throughout the year, with growth rates estimated at 7.1% for Q1, 6.9% for Q2, and 7% for both Q3 and Q4.
CPI Inflation Forecast: The Consumer Price Index (CPI) inflation for the fiscal year 2024-25 is anticipated to stand at 4.5%. Quarterly inflation forecasts paint a nuanced picture, with projections at 4.9% for Q1, 3.8% for Q2, 4.6% for Q3, and 4.5% for Q4.
Non-Policy Measures:
Sovereign Green Bonds Trading Scheme: The RBI intends to introduce a scheme for the trading of sovereign green bonds at the International Financial Services Centre (IFSC), fostering sustainable finance initiatives.
Retail Direct Scheme Access: A mobile application will be launched to facilitate access to RBI’s Retail Direct Scheme, enabling retail investors to participate in the Government Securities (GSec) market seamlessly.
Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) Framework Draft: A draft circular for the Liquidity Coverage Ratio framework for banks will be issued shortly, reinforcing liquidity management practices within the banking sector.
Rupee Interest Rate Derivative Products: Small finance banks will now have the authority to engage in dealing with rupee interest rate derivative products, enhancing their financial market participation.
UPI for Cash Deposit Facility: The utilization of Unified Payments Interface (UPI) for cash deposit facilities will be enabled, offering greater convenience and accessibility to banking services.
UPI Access for Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs): Third-party applications will now have access to UPI for facilitating transactions involving Prepaid Payment Instruments (PPIs), furthering the integration of digital payment systems.
Distribution of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs): The distribution of Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) will be facilitated through Non-bank Payment System Operators, paving the way for the adoption of digital currencies in the financial ecosystem.
The outcomes of the RBI MPC meeting underscore a nuanced approach towards monetary policy formulation and regulatory initiatives. With a focus on maintaining stability while fostering growth and innovation, the RBI’s decisions aim to navigate the complexities of the economic landscape effectively. As India charts its course through the fiscal year 2024-25, the implementation of these measures is poised to shape the trajectory of the nation’s economy and financial ecosystem.